|
Aircraft Carrier: Guardian of the Seas
Runtimes: 25 and 43 minutes Release Date: June 17, 2016 (short), May 26, 2017 (long) Production Companies: K2 Films and Giant Screen Films Writer/Director: Stephen Low Executive Producer: Bob Kresser, Stephen Low, and Don Kempf Producers: Mark Krenzien, Pietro L. Serapiglia, Andy Wood, and Mark Kresser Narrator: Maurice Dean Wint Formats: 2D, 3D, HD, 2K, 4K, fulldome conversion, 1570 Synopsis: The mission to protect and defend the world's oceans has become far more complex and challenging in recent years, and naval aviation has become increasingly vital to success. One of the greatest engineering feats in history, the modern U.S. nuclear carrier is a masterpiece of technology, and the flagship of the fleet. With RIMPAC, the world’s largest and most comprehensive international maritime training exercise providing a stunning visual context for the story, find yourself aboard the carrier alongside the 5,000 highly skilled sea and air personnel conducting flight operations in the midst of the simulated war exercises taking place there. Rarely has there been a topic so visually suited and compelling for IMAX® and other giant screen theaters. |
The Navy operates a wide range of sophisticated equipment that is featured in the film...
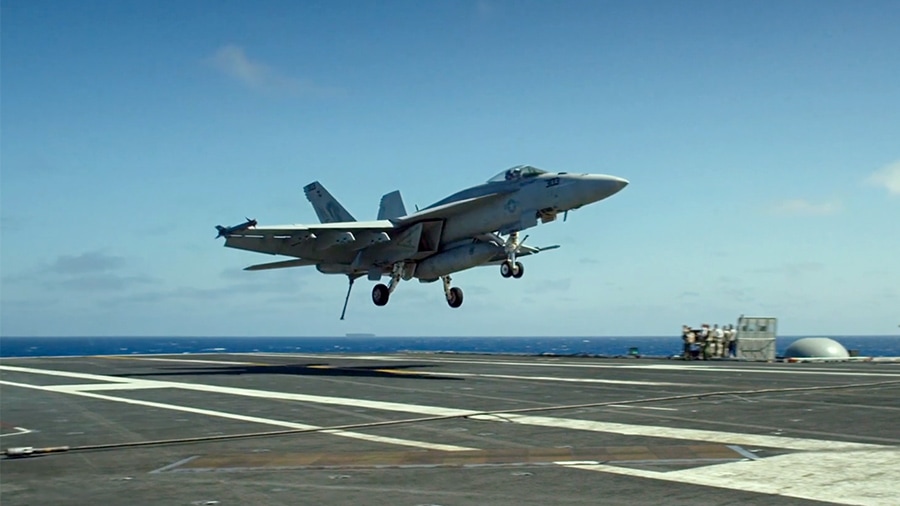
AIRCRAFT CARRIER (Nimitz- and Ford-class)

One of the greatest engineering feats in history, the modern Nimitz-class carrier is a masterpiece of technology, and the flagship of the fleet. It is capable of housing a crew of over 5,000 men and women, and nearly 90 individual aircraft. With an overall length of 1,092 feet and full-load displacement of over 100,000 long tons, they have been the largest warships built and in service, although they are being eclipsed by the upcoming Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carriers. The new Ford-class carriers will introduce new technologies such as the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System, advanced arresting gear, automated systems, and more.
F-35 Lightning II Fighter (A, B, and C Variants)
|
|
The F-35 Lightning II is a single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft designed for many missions with advanced, integrated sensors built into every aircraft. Missions that were traditionally performed by small numbers of specialized aircraft, such as intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance and electronic attack missions can now be executed by a squadron of F-35s, bringing new capabilities to many allied forces.
Three variants of the fighter are being produced by Lockheed Martin: F-35A conventional take-off and landing (or CTOL) F-35B short take-off vertical landing (or STOVL) F-35C carrier-based Catapult Assisted Take-Off Barrier Arrested Recovery (CATOBAR) |
Helmet Mounted Display System for F-35
Designed along with the F-35 is a Helmet Mounted Display System that provides pilots with unprecedented situational awareness. All the information pilots need to complete their missions – airspeed, heading, altitude, targeting information and warnings – is projected on the helmet’s visor, rather than on a traditional Heads-up Display. This approach greatly reduces the pilot’s workload and increases responsiveness. Additionally, the F-35’s Distributed Aperture System (DAS) streams real-time imagery from six infrared cameras mounted around the aircraft to the helmet, allowing pilots to “look through” the airframe. The helmet also provides pilots night vision through the use of an integrated camera.
PRATT & WHITNEY F135 TURBOFAN ENGINE
|
The Pratt & Whitney F135 two-spool afterburning turbofan engine powers all three variants of the F-35 Lightning II Joint Strike Fighter. The F135 propulsion system is the most powerful fighter engine ever developed.
The F135-PW-100 powers the U.S. Air Force F-35A Conventional Take-Off and Landing (CTOL) variant and provides 28,000 pounds of thrust or as much as 43,000 pounds with afterburner. The more complex (and almost twice as expensive) F135-PW-600 system is used on the Marine Corps F-35B Short Take-Off and Vertical Landing (STOVL) variant. The system is basically an F135 engine coupled to a lift system. The lift system is comprised of a lift fan, a driveshaft, the 3 Bearing Swivel Module (3BSM), and two roll posts. The driveshaft connects the F135 engine to the lift fan and delivers as much as 29,000 shp. The lift fan provides the forward vertical lift. It is a 50-inch, two-stage counter-rotating fan, which is able to deliver more than 20,000 pounds of thrust. The 3BSM is a swiveling jet pipe, which redirects the main engine thrust downward to provide the rear vertical lift. It can rotate 95 degrees in 2.5 seconds and directs 18,000 pounds of thrust. The F135-PW-400 powers the Navy's F-35C Carrier Variant (CV) and provides 28,000 pounds of thrust or as much as 43,000 pounds with afterburner. |
F-35 ELECTRONIC WARFARE TECH BY BAE SYSTEMS
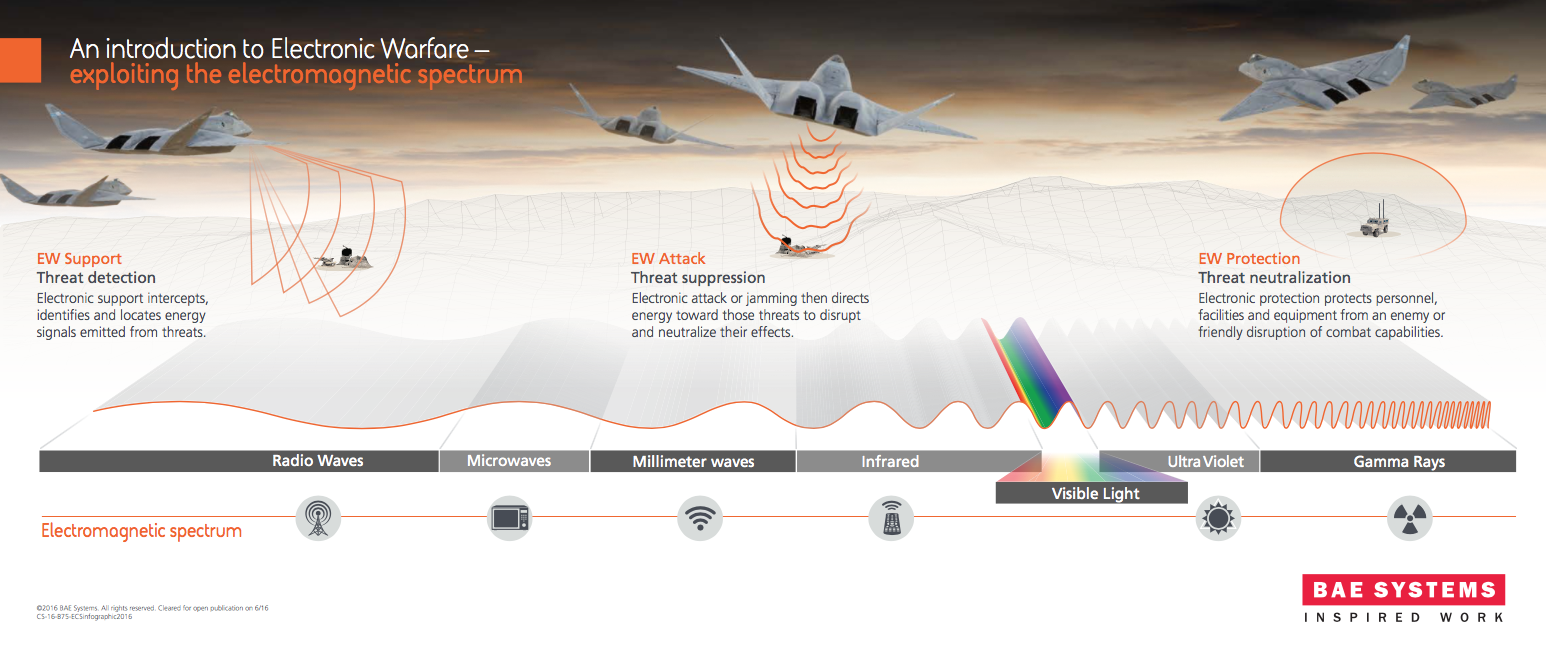
BAE Systems has introduced electronic warfare technology to the F-35 Lightning II Joint Strike Fighter, exploiting the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electronic support intercepts, identifies and locates energy signals emitted from threats. Electronic attack or jamming then directs energy toward those threats to disrupt and neutralize their effects. Electronic protection protects personnel, facilities and equipment from an enemy or friendly disruption of combat capabilities.
Electronic support intercepts, identifies and locates energy signals emitted from threats. Electronic attack or jamming then directs energy toward those threats to disrupt and neutralize their effects. Electronic protection protects personnel, facilities and equipment from an enemy or friendly disruption of combat capabilities.
F/A-18 SUPER HORNET
|
A supersonic, all-weather multirole fighter, the Super Hornet is a workhorse in the Navy, capable of landing and taking off from an aircraft carrier. Its twin engines produce a combined 44,000 pounds of thrust and a Mach 1.8 top speed. Moreover, the Super Hornet has 11 weapons stations, which allows the aircraft to carry over 400 configurations of air-to-air and air-to-ground ordnance.
|
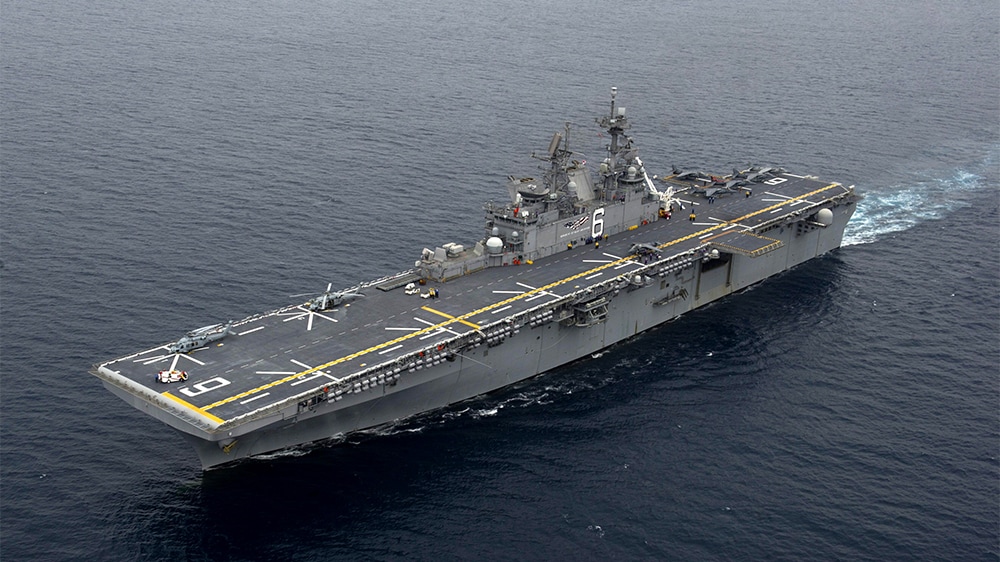
AMPHIBIOUS ASSAULT SHIP - USS AMERICA (LHA-6)
|
USS America (LHA-6), the fourth American warship to be named for the United States of America, is the first of the America-class amphibious assault ships for the U.S. Navy. Her mission is to act as the flagship of an expeditionary strike group or amphibious ready group, carrying part of a Marine expeditionary unit into battle and putting them ashore with helicopters and V-22 Osprey tilt-rotor aircraft, supported by F-35B Lightning II aircraft and helicopter gunships.
|
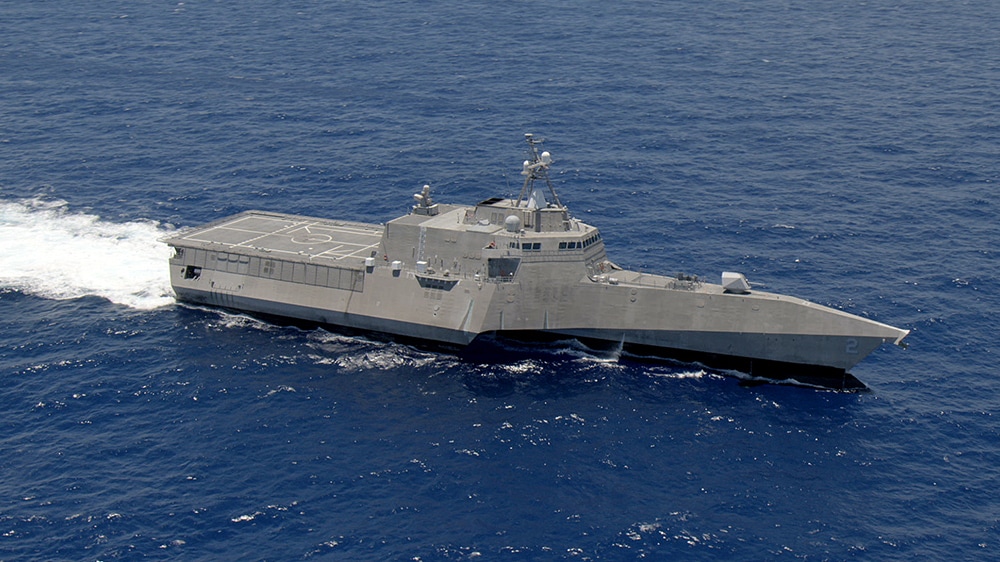
Littoral Combat Ship
|
The littoral combat ship (LCS) is a class of relatively small surface vessels intended for operations in the littoral zone (close to shore) by the United States Navy. The Freedom class and the Independence class are the first two LCS variants. Both are slightly smaller than guided missile frigates and have been likened to corvettes. They have the capabilities of a small assault transport, including a flight deck and hangar for housing two SH-60 or MH-60 Seahawk helicopters, a stern ramp for operating small boats, and the cargo volume and payload to deliver a small assault force with fighting vehicles to a roll-on/roll-off port facility.
|
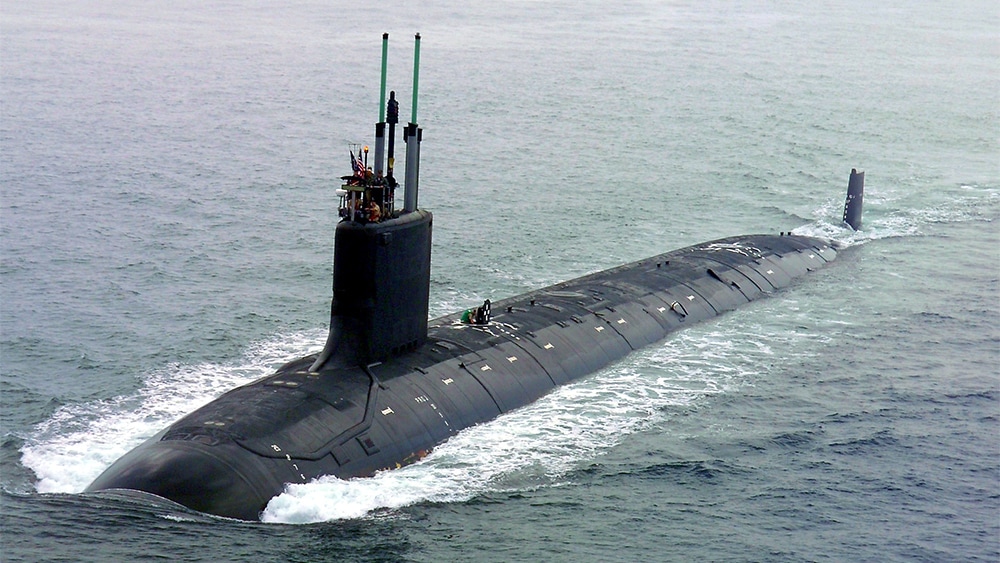
SUBMARINE (Virginia-class)
|
The Virginia class, also known as the SSN-774 class, is a class of nuclear-powered fast attack submarines (hull classification symbol SSN) in service with the United States Navy. The submarines are designed for a broad spectrum of open-ocean and littoral (shallow coastal water) missions, and complement the exercises conducted at RIMPAC.
|